Ways to add CSS
Ways to add CSS
There are three different ways to add CSS to an HTML page, which are:
- Inline CSS
- Internal CSS
- External CSS
Inline CSS
Inline CSS is used to add custom properties to specific elements. The added style will only reflect on that particular element only.
To use inline CSS, Insert the "style" attribute within the HTML element's opening tag.
Consider the code snippet:

Here, the inline style of color: purple is attached to only the h1 tag.
Note: The downside of using inline CSS is, that once the project complexity increases, it will become difficult to manage the styles of each and individual elements.
Internal CSS
Internal CSS is used to apply custom style to the multiple elements on the same page. The style can be used throughout the HTML page.
Consider the code snippet:

Here, in the style block, selector p will target all p tags and assign them color:red.
Note: The <style> block should always be in the <head> section.
External CSS
External CSS works similarly to internal CSS but with a twist. Instead of adding the styles within the HTML file, we create a separate file with .css extension. This file will hold all the styling details. Then, we link this file to the HTML page, giving it the instructions on how to look.
The following video will explain, how to link a CSS file to HTML.
There is a new <link> tag in the head section, and this link tag has rel and href properties.
The following points will explain each keyword's meaning:
- <link>: This tag is used to create links between different resources, like stylesheets, fonts, and more. In our case, we are using a link tag to link the CSS file with the HTML file.
- rel="stylesheet": rel stands for relationship, this defines the type of relationship between the HTML document and the linked resource. When set to "stylesheet", it specifies that the linked resource is a stylesheet that will be used to style the HTML content.
- href="style.css" : The href attribute stands for "hypertext reference." It specifies the path or URL to the external resource we want to link. In this case, it's the path to the external CSS file called "style.css".
Consider the code snippets:
These code snippets will generate this page:
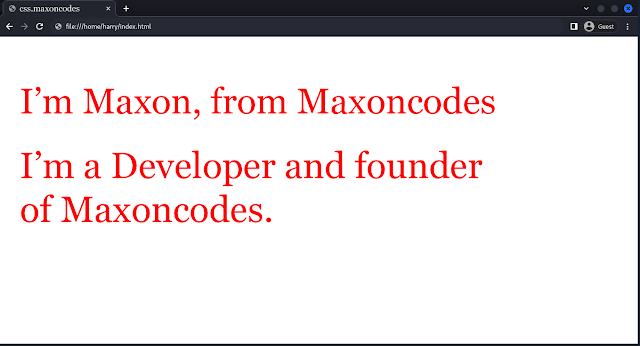
This approach enables to use of the same CSS to multiple HTML files, wherever the same custom style is required.
This is helpful when we have to maintain consistency on our web pages and want to use the same CSS styles across multiple pages.
Note: The precedence is Inline CSS > Internal CSS > External CSS. If we define the same property with different property values in three different ways, the element will have the property value of inline CSS.
Feel free to explore the CSS Wikipedia page to gain more insights about CSS working.