CSS Z-index
CSS Z-index
When there are multiple overlapping elements, the z-index helps in deciding the order of their visibility. The element having the highest value of z-index is shown first, followed by the other elements.
Eg:
Output:
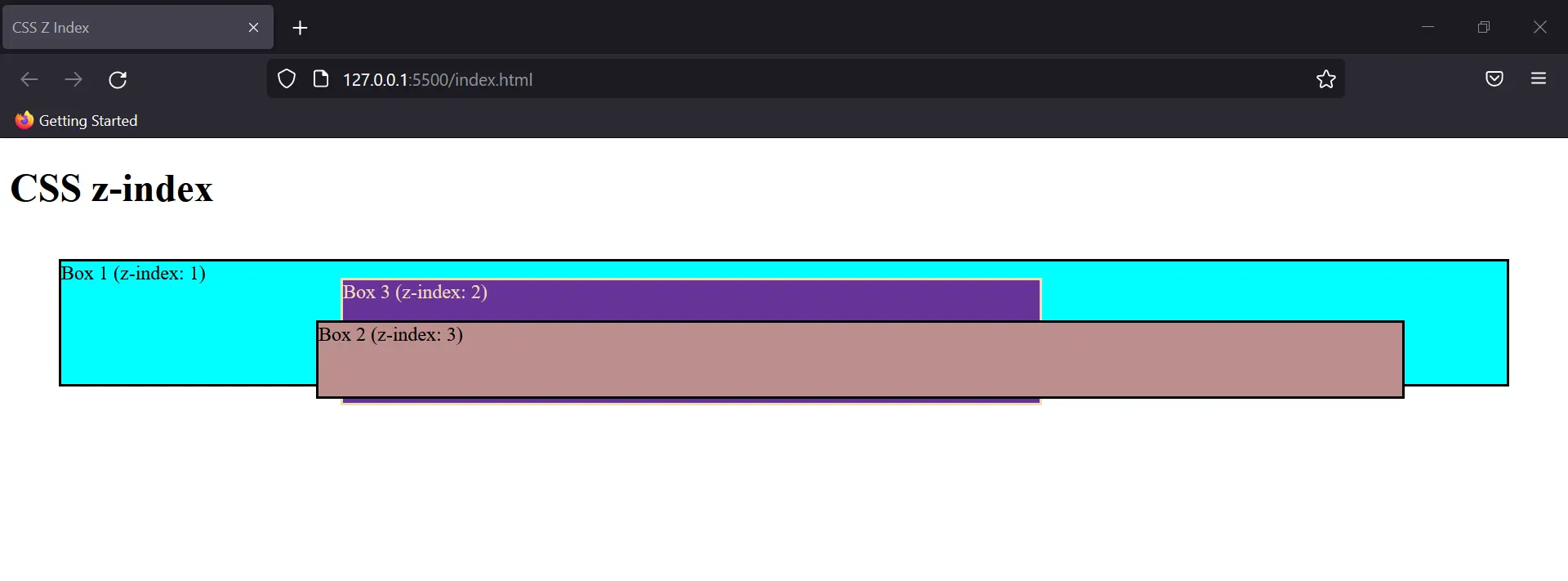
When z-index isn’t used, the element defined in the last is shown on the topmost. Therefore Box 3 would’ve been visible to us.