CSS Positioning
The CSS positions allow you to precisely control the placement of an element on the web page.
It helps to determine how elements are placed inside the container element and how they interact with the other elements on the page.
There are various types of position property values, such as:
Static(Default)
The elements are positioned according to the normal flow of the document.
Syntax:
Example:
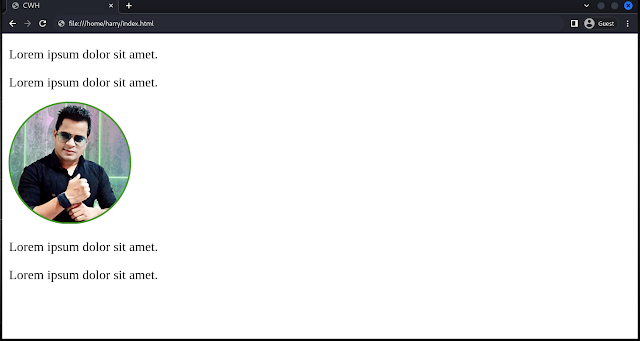
Relative
Elements are positioned relative to the normal position in the document.
You can use the top, right, bottom, and left properties to move the element from its original position.
Syntax:
Example:
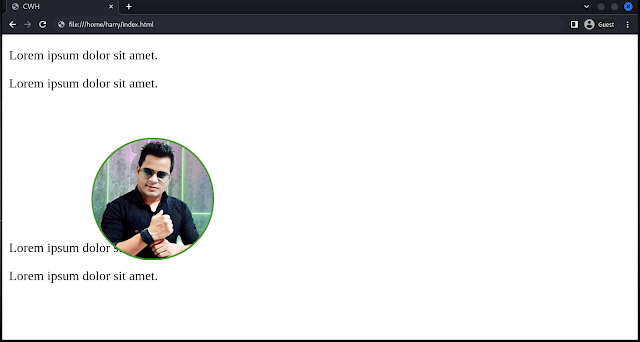
Here you can see that the image is repositioned from its original place, and the gap is not filled by another element.
Absolute
Elements are positioned relative to the closest positioned ancestor (parent), which means we need to have a parent element with a positioning other than 'static'.
Note: An absolutely positioned element is removed from the normal flow.
Example:

Explanation:
Here, as we have set position relative to the body and absolute to the about section, the about section position can be manipulated with the left of top, left, right, and bottom.
Fixed
Elements are positioned relative to the viewport (screen) and do not move when the page is scrolled.
This is useful for creating elements like fixed headers or footers.
Example:
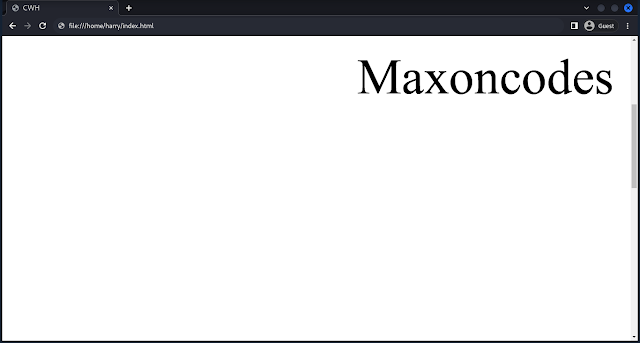
Here, the image position will be fixed.
Float
The float property is used to shift an element to the left or right within its containing element. For more details, follow CSS Float.
Sticky
Position sticky is a hybrid between 'relative' and 'fixed'.
It allows an element to become "stuck" to the top or bottom of its container when scrolling, but it behaves like relative positioning within the container until it reaches a specified offset.
Example:


